Easy Doppler principles from mini
Thanks to JAYPEE PUBLISHERS & Dr Satish Bhargava
FOR permission to use this material for medical reference
1.4 a Triphasic sprectrum
1.4 b after exercise pronounced forward flow component in diastole
1.4 c low peripheral resistance
1.5 b moderate pulsatility
1.5 c high pulsatility
1.5 low pulsalitity -int carotid art
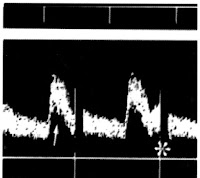
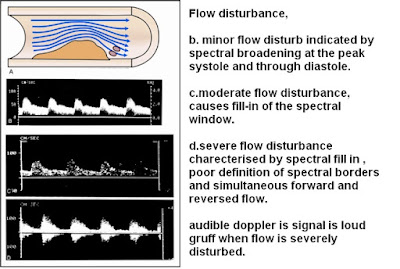
1.7 a.disturbed flow
1.8 NORMAL BIFURCATION FLOW DISTURBANCE
1.14.LOCAL EFFECT OF ARTERIAL STENOSIS
A.high velocity in the narrowed portion of the arterial lumen generate an area of aliasing (arrow) within the stenotic lumen,
B.disturbed flow in the post stenotic area generates a mixture of colors(arrow),
C.dopplor spectral analysis shows markedly elevated velocity at the peak systole (350.7cm/sec) and end diastole (116.9cm/sec),
D.Severe flow disturbance is evident in the post stenotic region, as indicated by simultaneous forward and reverse flow,spectrum fill-in, poor definition of the spectrum margins.
WAVEFORM in stenosis
A.acceleration time is prolonged (0.15 sec) in the left kidney due to severe proximal renal artery stenosis.accelaration time is defined as time in secs taken by the blood flow to reach the PSV from the baseline .
B.Severely dampened dorsalis pedis artery waveform distal to femoral/ popliteal artery occlusion.
SPECTRAL WAVEFORM IN STENOSIS
A. Prestenotic spectrum from common carotid artery shows low systolic and diastolic velocity with filling of the spectral window.
B.intrastenotic spectrum shows mark elevation of flow velocity indicating turbulance,
Post stenotic spectral also shows filling of the systeloc window with broader and higher systolic peak than prestenotic area